Trainings
Soil Testing
Aggregate Stability Test: https://www.fao.org/fileadmin/
Using Soil As A Water Filter
Most Popular DIY Water Filter: Activated Charcoal Filter

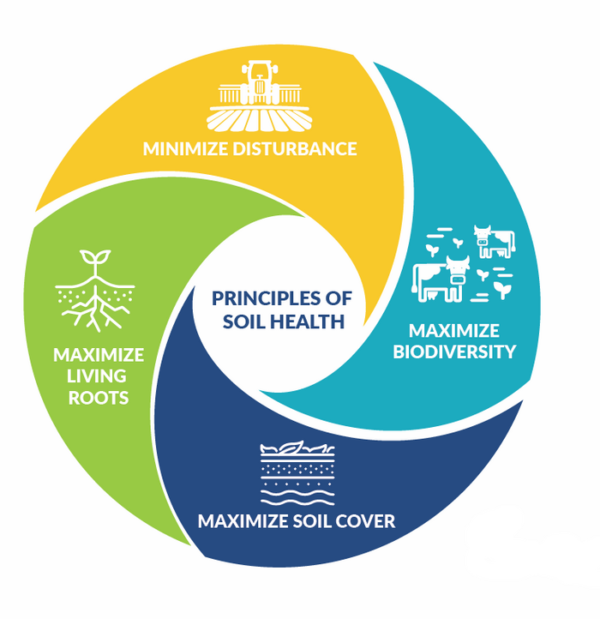
Maintaining Your Soil
Soil Contamination Testing
Logan Labs | Send them samples, and they will send you results.
Soil testing is an important part of creating a healthy ecosystem. Whether it be a backyard garden or a cash crop, the health of your soil matters. Watch the video to learn more about why you should soil test.
Soil and Plant Nutrient Testing Laboratory | Currently accepting new orders for ROUTINE SOIL ANALYSIS (including optional Organic Matter, Soluble Salts, and Nitrate testing), PARTICLE SIZE ANALYSIS, PRE-SIDEDRESS NITRATE (PSNT), and SOILLESS MEDIA orders ONLY. Please do not send orders for other types of analyses at this time.
Places to Buy Seeds
How to help your soil retain more water – https://plantcareforbeginners.com/articles/how-to-make-your-soil-retain-more-water
9 Ways To Nourish Your Soil
Mix in a specific amount in solid form, in soluble form (i.e. water), composting with decomposing fruit peels, grass clippings that have not been sprayed with any pesticide/insecticide/herbicide, fallen tree leaves, egg shells, coffee grounds, fish tank water, ground crustacean shells and more.
Always check the soil pH if you amend your soil.
Considerations: How slow or fast do you want the amendment released?
When making mulch, start with the right ingredients to add vitamins and other nutrients to your plants. Many of you will throw your banana peels away, but they make excellent natural fertilizers.
It’s not just the human body that needs potassium. Roses and some other beautiful flowers need it. Bananas are full of that nutrient—including the banana peel!
You don’t even need to add the peels to your mulch. Add them to the hole before you plant your flowers. They’ll degrade naturally and the soil around them will soak up the potassium.
In mulch, add them to the bottom, so they can compost naturally. The right compost ingredients can help build long-term fertility.
Save your coffee grounds or pick up a few bags of spent grounds from your local coffee shop. Most places will save the grounds and gladly allow you to tote them off for your garden.
Coffee has some nitrogen that slowly releases into the soil. It is also very rich in magnesium, copper, potassium, and phosphorus. You can even add it directly into the soil instead of composting. It will break down quickly when mixed in.
Commercially produced natural fertilizers often use a fish emulsion as a nutrient base. Fish manure has a balanced blend of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Many readers probably have a fishtank in the house that needs regular cleaning.
Next time you change the water, save it in a bucket. You can use this water to fertigate your plants with liquid nutrients. I do have one word of caution here.
If you recently treated your fish with antibiotics or any other medicine do not use the water. You don’t want to kill off the healthy soil bacteria with medicated water.
Dry out your egg shells and crush them up when you get a few dozen. You can mix them directly into the soil or add to your compost. There is a very small amount of nitrogen and phosphorus here, but mostly you are getting calcium.
If you have laying chickens, you can also use crushed eggshells to supplement their calcium needs. Speaking of chickens, why not add animals to your fertilization program?
Some manure can be added directly to your garden like rabbit pellets. However, others are “hot” and must be allowed to compost before adding to your garden. High nitrogen levels from hot manure can burn your plants.
Livestock manure can be composted to prevent it from burning plants. However, another strategy with chickens is to simply place their living area uphill from your garden. The nutrients will slowly leach downhill preventing too much nitrogen from getting to your plants at once.
Only do this if you are rotating them through an area and not putting too much stress on the land. You can still burn your plants with this method if your stocking densities are too high.
However, if you have a backyard flock of just a few birds, this usually works just fine.
Gardeners are always told that weeds are bad. Sure, they take up nutrients and space from our plants but they can also offer some benefits.
When it comes to the best natural plant fertilizer, you’ll want to consider nettles, burdock, and other similar weeds.
Adding them into compost can even speed up the breakdown process in your own backyard. Greens from weeds can provide a nitrogen source for your compost. Just be sure to always use hot composting methods to kill any weed seeds.
The best weeds are those that haven’t flowered yet. Pull them out of the garden and let them dry out in the sun. They can then be thrown into the compost and allowed to degrade there.
You will need to make sure the roots have completely dried to avoid them taking over your compost!
Yes, this really does sound disgusting. Our bodies actually let out some of the best fertilizers for plants! Specifically, let’s talk about urine. This is sterile, but only if it comes from a healthy, virus-free body.
If you’re ill then you will want to keep the urine out of your compost heap because it will be getting rid of the toxins in the body. Urine has nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorous in larger amounts than the majority of store-bought fertilizers (yes, even the natural ones).
It is very concentrated and will burn your plants if not diluted. You’ll only need one cup of urine to eight cups of water.
Even if you don’t have livestock, you’ll want to consider getting some food for your compost pile. Chicken or Horse feed is full of protein for the animals, which means it’s perfect for your plants.
Alfalfa pellets or vegetarian chicken feed is basically concentrated plant nutrients that readily compost when combined with a “brown” like shredded leaves or sawdust.
The problem with expired livestock feed is that pests will find your compost heap interesting. You’ll need to make sure you cover it until all the food is decomposed in the heap. These items just give you some of the best natural plant fertilizers that you will either already have or might buy.
You can also opt for store-bought natural fertilizers to keep your plants healthy and chemical free. Look for a company that is reputable and offers a data sheet listing ingredients.
Things like fish emulsion, bone meal, blood meal, kelp, and potash make excellent natural fertilizer ingredients.
Making Your Own Soil

DIY Potting Soil | Savvygardening.com
Considerations: location of whatever you’re planting (inside and/or outside)
- Measuring container like a 5 gallon bucket or large pot
- Shovel
- Mixing container like a large garden tub, wheelbarrow, or tarp
- Water (if ingredients are dry)
- Coco coir or peat moss
- Potting soil
- Composted soil or composted manure
- Perlite
- Vermiculite
- Measure 2 containers full of coco coir and place in your mixing container. If it feels dry, add a little water to moisten it. If you’re using peat moss, measure 2 containers full into your mixing container.
- Measure 2 containers full of composted soil or composted manure into your mixing container
- Measure 1 container full of perlite into your mixing container
- Measure ½ container full of vermiculite into your mixing container
- Mix well with a shovel
Learn More
Soil courses: https://www.soilfoodweb.com
Soil Management: https://www.sare.org/sare-
